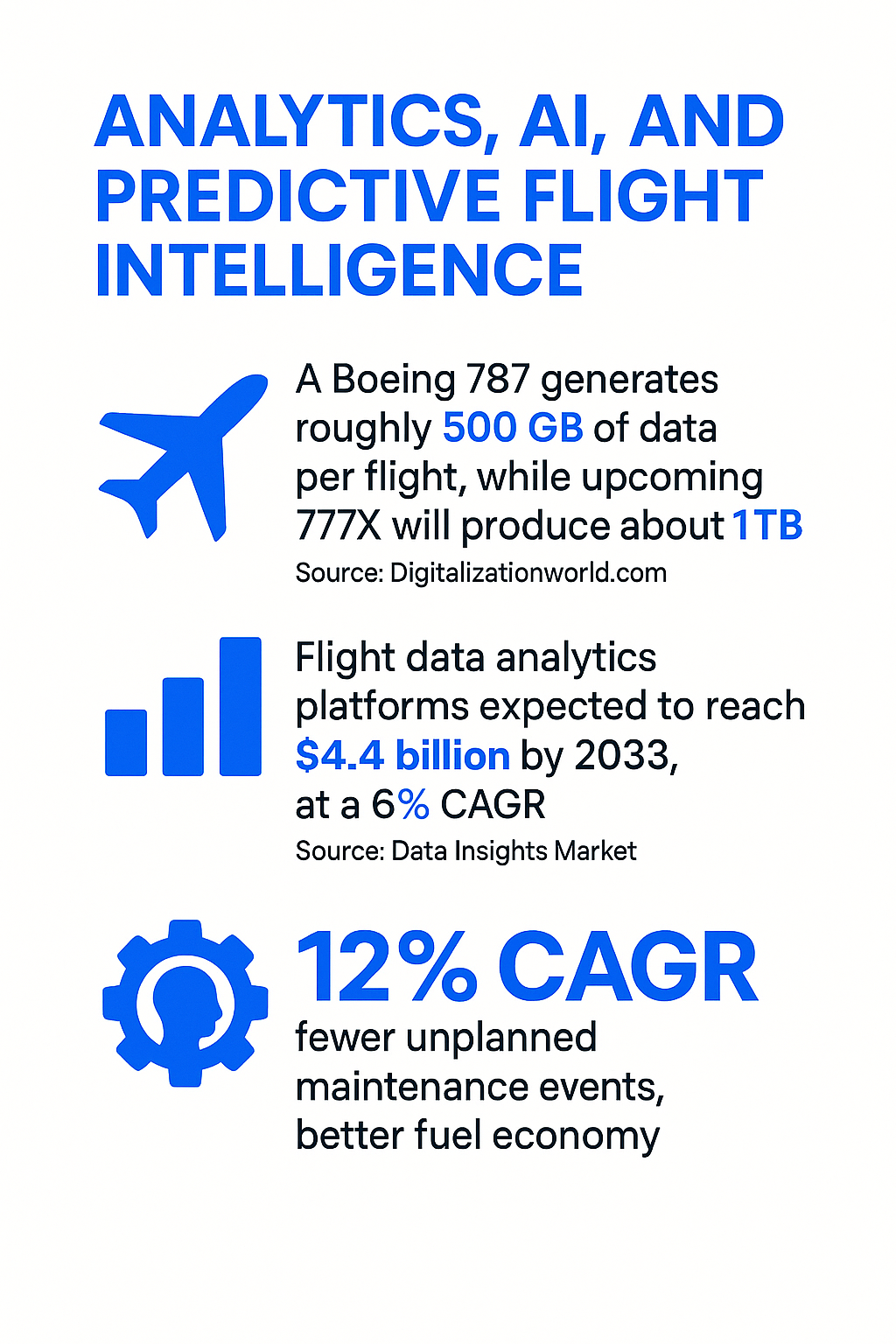
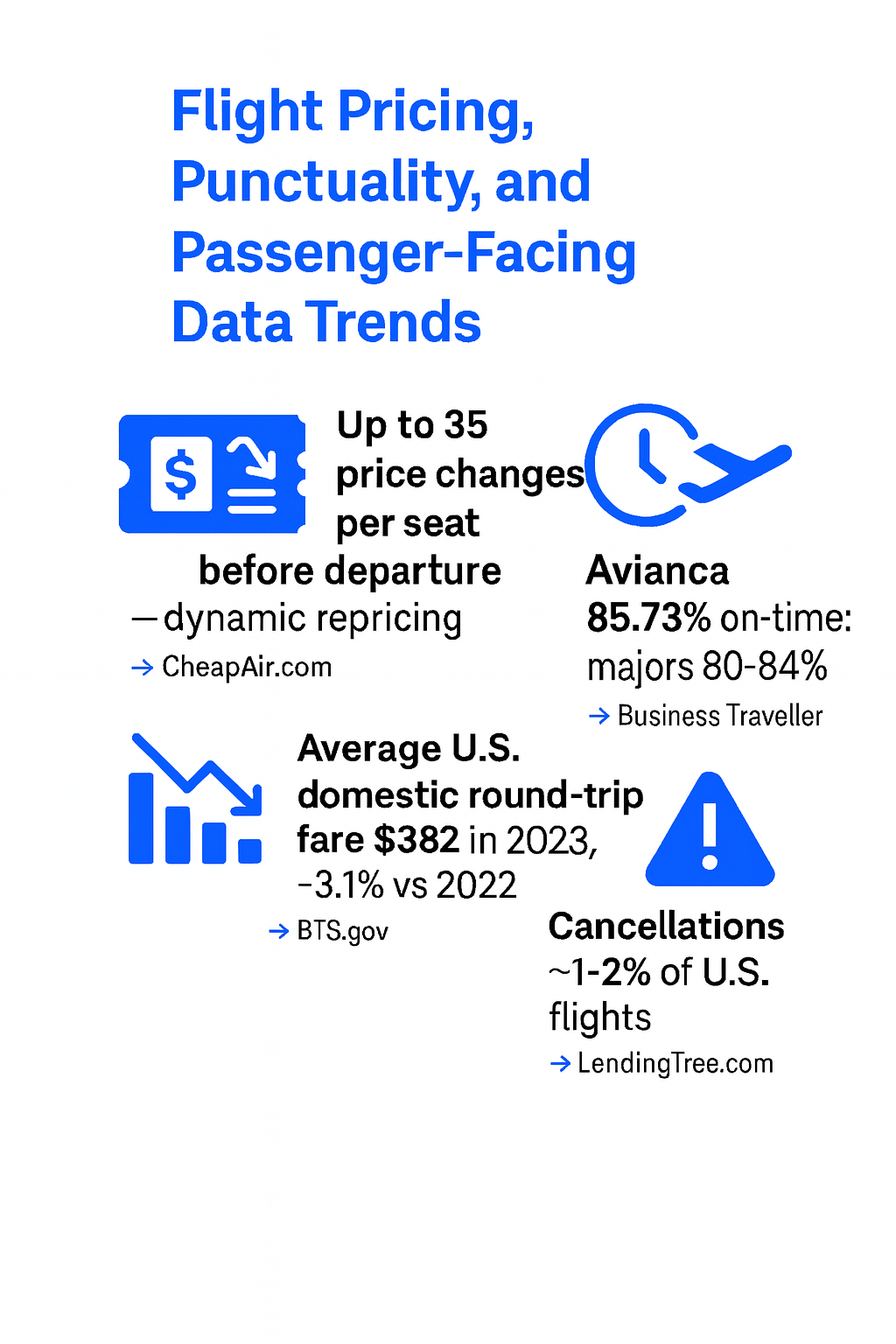
Looking for the latest Flight Data Monitoring statistics and trends? You’re in the right place. Flight data isn’t just numbers on a dashboard but the pulse of modern aviation. From safety systems to pricing algorithms, every decision in the air and on the ground relies on accurate, real-time data. At FlightAPI, we work with this data every day. Our APIs power everything from flight pricing and status updates to airport schedules, helping businesses and developers access flight data. That firsthand experience gives us a clear view of just how crucial flight data monitoring has become not only for safety but for smarter, more efficient operations across the entire aviation chain. To help you get a full picture of where things stand, we’ve pulled together the most recent and relevant flight data monitoring statistics. These numbers reveal how fast the field is growing, what technologies are leading the charge, and how the industry is turning information into intelligence. Let’s take a closer look. Market Expansion and Key Growth Drivers 📊 The global Flight Data Monitoring (FDM) market was valued at around $5.03 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach roughly $8.2 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of about 5%.→ Source: Straits Research 📊 That kind of steady growth doesn’t happen by accident. It’s the result of several forces aligning at once. Air travel demand continues to climb at a historic pace. According to IATA, global passenger traffic is expected to more than double by 2036, a projection that’s pushing airlines to expand fleets and adopt smarter oversight tools.→ Source: Straits Research Safety regulations are another driver. Aviation authorities like ICAO, FAA, and EASA are tightening standards, encouraging or requiring airlines to operate formal FDM or FOQA (Flight Operations Quality Assurance) programs. These systems interpret data and spot deviations long before they become incidents. The tragic cases of Air France 447 (2009) and MH370 (2014) showed how missing or incomplete flight data can delay answers. Since then, the adoption of continuous monitoring systems has become near universal among major carriers. The overall pattern is clear. FDM is no longer just a safety initiative; it’s a strategic asset. Airlines are investing in data because it helps them fly smarter, not just safer. ADS-B and the Era of Real-Time Flight Tracking 📊 By late 2025, roughly 97.2% of aircraft and 98.9% of flights in the Eurocontrol area were equipped with ADS-B transmitters.→ Source: Eurocontrol 📊 ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast) has transformed flight visibility. Nearly every commercial aircraft now broadcasts its GPS-derived position in real time. In the U.S., the FAA’s 2020 ADS-B Out mandate accelerated adoption, and by mid-2024, around 168,000 registered aircraft had ADS-B installed that cover virtually all commercial airliners and much of general aviation.→ Source: FAA.gov 📊 This data doesn’t just sit in databases. It powers global networks that track the pulse of aviation minute by minute. On July 6, 2023, Flightradar24 recorded 134,386 commercial flights in a single day, the highest count since the platform began operations.→ Source: Paxnews.com 📊 Platforms like FlightAware have built massive receiver ecosystems — over 40,000 active ADS-B stations worldwide as of 2025 — creating a live map of the skies.→ Source: FlightAware Blog Space-based systems, such as Aireon, now close the gaps over oceans and remote areas. For airlines, that means fewer blind spots and faster anomaly detection. For the public, it’s transparent, real-time access to flight activity on a scale that would’ve been unthinkable just a decade ago. Analytics, AI, and Predictive Flight Intelligence 📊 A Boeing 787 generates roughly 500 GB of data per flight, while the upcoming 777X will produce about 1 TB.→ Source: Digitalisationworld.com This is a goldmine. Airlines are learning to convert this constant stream of sensor data into actionable insights. Predictive analytics now sits at the center of flight data strategy, helping operators move from reactive to proactive safety and maintenance. 📊 The analytics market is expanding even faster than data collection itself. 📊 Flight Data Analytics Platforms are expected to reach $4.4 billion by 2033, with an estimated 6% CAGR, as airlines invest in intelligence rather than raw storage.→ Source: Data Insights Market 📊 These systems crunch everything from fuel burn to flap cycles, flagging inefficiencies and predicting potential failures. The payoff is real: fewer unplanned maintenance events, better fuel economy, and more consistent on-time performance. Some estimates suggest double-digit growth (around 12% CAGR) in the broader flight data analysis market through the next decade.→ Source: Data Insights Market Major players like Safran, Honeywell, Airbus (via NAVBLUE), and Boeing are integrating AI to forecast and optimize. Meanwhile, newer firms are pushing into real-time engine health monitoring and cloud-based fleet intelligence. Collectively, this shift is redefining FDM from a compliance function into a strategic driver of profitability and reliability. Flight Pricing, Punctuality, and Passenger-Facing Data Trends While the cockpit gets smarter, data is reshaping the passenger experience too. Flight prices and punctuality are now as measurable as altitude or airspeed. 📊 A single airline seat can change price up to 35 times before departure, driven by automated repricing algorithms that respond to demand and inventory in real time.→ Source: CheapAir.com 📊 This volatility has created an entire layer of consumer analytics, such as Google Flights, Hopper, Skyscanner, and similar platforms that track fare movements minute by minute. In the U.S., average domestic round-trip fares hit $382 in 2023, a 3.1% decrease from 2022 (inflation-adjusted), showing how data transparency helps travelers spot opportunities.→ Source: BTS.gov 📊 On the operational side, punctuality data has become a reputation metric. 📊 Avianca topped global on-time rankings in 2023 with 85.73% of its 213,000 flights arriving as scheduled, while major U.S. airlines averaged between 80% and 84%.→ Source: Business Traveller 📊 Even small delays create ripple effects, so airlines use real-time predictive models that factor in aircraft positioning, weather, and air traffic flow. Cancellations now remain relatively low, usually around 1–2% of U.S. flights, thanks to stronger predictive planning.→ Source: LendingTree.com What this means for passengers is

Finding reliable flight price data may seem simple until you actually start searching. Then you realize how crowded the space...